TypeScript Guide for beginners with examples(tutorial)
In this tutorial, we are going to learn about what is TypeScript and how to use typescript in our projects.
What is TypeScript?
A typescript is a superset of JavaScript where it compiles down into plain JavaScript.
-
TypeScript is developed and maintained by Microsoft.
-
TypeScript provides us static type checking to our JavaScript code.
-
TypeScript gives us user-friendly errors during compile time.
-
We can use new JavaScript features and future proposals in TypeScript.
Getting started
Let’s install the typescript compiler by using the node package manager(npm).
Run the following command to install typescript compiler in your computer.
npm i -g typescriptif you are using a mac then you need to add
sudobefore the command
create a new directory in your machine by running the below commands.
mkdir learn-typescript
cd learn-typescriptNow open learn-typescript folder in your favorite code editor and create a new file called
dummy.ts.
.tsis a typescript extension.
Writing our first TypeScript code
Let’s write our first typescript code in our dummy.ts file.
let dummy: string = "Hello Boss";In the above code, we added a type annotation string so that dummy variable can only allow strings if we try to pass other than strings like numbers or arrays TypeScript compiler raise an error.
Compiling our TypeScript code
Let’s compile our TypeScript code by running the below command.
tsc dummy.ts #tsc : typescript compilerNow you can see a new file called dummy.js is generated by the typescript compiler which contains our pure JavaScript code.
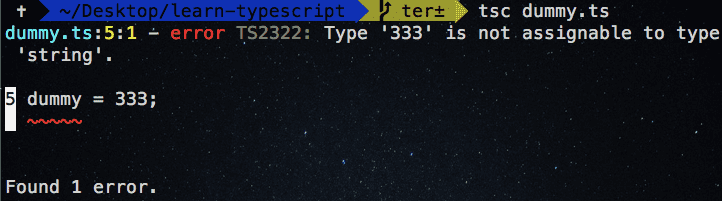
Let’s generate our first error by passing the wrong value to the dummy variable.
let dummy: string = "Hello Boss";
dummy = 333Have you seen typescript compiler generates an error “333” is not assignable to string?
Type Annotations
Type annotations mean we are taking the contract to variables or functions or objects can only accept particular types if we try to pass the wrong types we will get an error.
They are different types TypeScript provides us most of them have come from JavaScript types.
String type
A string is declared by using single quotes('') or doubles quotes(""). By using
string type we refer to string data type in typescript.
example:
let welcome:string = "welcome to reactgo.com"
// we can also use template strings in TypeScript
let name: string = `Gowtham`;
Number type
In TypeScript we have floating point numbers like same in JavaScript, these floating point numbers get the type number in TypeScript.
let a: number = 1 ;
Boolean type
Boolean data type has only two values which are either true or false in typescript we use type boolean to accept boolean values.
let isActive: boolean = true;Arrays
In TypeScript, they are two ways to accepts array types.
The first way is element type followed by array [].
// fruits variable can only accept an array of string types.
let fruits:string[] = ['apples','apricots','avocados'];
In the above code, we have added a string type with array[] so that fruits variable can only accept an array with strings.
The second way uses the generic array type Array<elementtype>
let fruits:Array<string> = ['apples','apricots','avocados'];
// numbers variable can only accept array of numbers
let numbers:Array<number> = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8];
Tuple
In TypeScript, we have tuples it means we can only allow a fixed number of element types to the array.
// we declared a tuple
let user:[string,number,string];
// intializing the values
user = ['baby',33,'programming']; // TypeScript is happy now
We declared a tuple with three types string,number and string so that we have a fixed length of the array with three types if we try to initialize with wrong types or more than three elements TypeScript will raise an error.
// we declared a tuple
let user:[string,number,string];
// intializing the values
user = ['baby',33,'programming']; // TypeScript is happy now
//re intializing with wrong values
user = [33,'baby',1]; // Error
Any type
Sometimes we are not sure what type of data we can get to the variables in that cases TypeScript provide us an any type.
let isActive:any = false; // boolean
isActive = "Do your work"; // stringany type usage in arrays.
let user:any[] = ['1233','king',39,true]In the above we used any type because we are not sure exactly what type of data we can get
to user array.
Function types
Let’s see how to add types to the functions.
// function with two parameters are number type
function add(a:number,b:number):number{
return a+b;
}Here we have added types to the function parameters and return type number.
we optionally leave return type to the functions because typescript can figure out return type automatically by looking through the return statements of the function.
Let’s create a fully typed function because in the above code we have just created a function with types.
let add:(a:number,b:number)=>number;
add = function(a:number,b:number):number{
return a+b;
}
add(1,2) //correct
In the above code, we exactly specifying what type does add function looks like.
Optional and default parameters in functions
In typescript, every parameter is strictly required if you fail to pass any parameter typescript gives us an error.
To make the function parameters optional we need to add ? at the end of the parameter.
optional parameters example
function welcome(name: string, age?: number): string {
if (name && age) {
return `Welcome ${name} and ${age}`
} else {
return `Welcome ${name}`
}
}
welcome('gowtham') // ok
welcome('gowtham',22) // ok
welcome('gowtham',22,'lol') // error Expected 1-2 arguments, but got 3
In the above code, we have added ? at end of the age parameter so that it becomes optional.
default parameter example
function getLength(arr: number[], length = arr.length) {
return length
}
getLength([1,2,3,4,5])Void type
void means the absence of returning any type, for example, a function that doesn’t return any type of value.
function alertHello():void{
alert('Hello')
}alertHello function doesn’t return any value.
Never type
The never is a return type of the function, arrow functions which always throws an exception.
A function that never reaches to the endpoint
// throw an exception
function error(err:string):never{
throw new Error(err);
}
// while loop never stops
function infinteLoop():never{
while(true){
}
}Interfaces
Interfaces help us to design the particular shape of data.
Let’s create an interface now.
interface User {
name: string
active: boolean
}
let user: User = {
name: "gowtham",
active: true
}In the above code, we have created an interface User with two properties where name property type is string and active property type is boolean.
Now the user object should always satisfy the shape of the interface.
We can also extend the interfaces by using extends keyword.
interface User {
name: string
active: boolean
}
// extending the User interface
interface AdminUser extends User {
id: string
}
let user: User = {
name: "gowtham",
active: true
}
// admin object should have properties
//present in User interface + AdminUser interface
let admin: AdminUser = {
name: "john",
active: true,
id: "3232hejdjdjf"
}Here we created a AdminUser interface by extending the User interface so that now admin object
shape should be combination of User interface plus AdminUser interface
Enums
Enums are set of named constants which are created by using enum keyword.In TypeScript we have string enums and numeric enums.
numeric enums
enum Day {
Monday,
Tuesday,
Wednesday
};
console.log(Day.Monday) // 0
console.log(Day.Tuesday) //1
console.log(Day.Wednesday) //2We have created a numeric enum Day by default first enumerator should be initialized with value 0
and auto-incrementing the next enumerators by 1 like Monday:0,Tuesday:1,Wednesday:2.
string enums
enum Colors{
Red = "#FF0000",
Green= "#008000",
Blue = "#0000FF"
}
In string enums we need to initialize a constant value like in the above code we have created a Colors enum with three enumerators.