How to build a simple GraphQL api using graphql-yoga and Nodejs
In this tutorial, we are going to build a simple todos API by using the GraphQL and graphql-yoga server.
Note: if you don’t know about what is Graphql then refer to my previous tutorial Graphql intro
Requirements
- Nodejs
First, we need to install a graphql-yoga package by using npm or yarn.
mkdir graphql-api
cd graphql-api
npm i -y
npm i graphql-yoga
graphql yoga package helps us to create the graphql server with the minimal setup.
Now, create a new file called app.js and add the below code.
const { GraphQLServer } = require('graphql-yoga');
//sample data
let todos = [
{
id: 1,
title: "This is my todo",
body: "sample content in id 1"
},
{
id: 2,
title: "This is my second todo",
body: "sample content in id 2"
},
{
id: 3,
title: "This is my third todo",
body: "sample content in id 3"
}
]
In the above code first, we require the graphql-yoga package and our todos are added inside the array because we are not using any database.
Next, we need to create the type definitions using graphql Schema definition language(SDL).
const typeDefs = `
type Todo {
id: ID!
title: String!
body: String!
}
type Query{
getAlltodos : [Todo!]!
}
`Here we created a Todo type which contains three fields id,title, body it means our todo data must be in this shape.
On Query type, we created getAlltodos field which returns back an array of todos.
Now we need to create the resolvers. Which helps us to resolve the particular query fields in the Schema.
const resolvers = {
Query:{
getAlltodos(){
return todos
}
}
}
The resolver function and Query field should have the same name otherwise graphql gives you an error.
Finally, step to turn on the server.
const server = new GraphQLServer({
typeDefs, resolvers, context: {
//if we pass anything here can be available in all resolvers
}
})
server.start(() => console.log('Server is running on localhost:4000☄'))Now in your terminal run node app.js and navigate to localhost:4000 in your browser.
This a graphql playground which helps us to test our data.
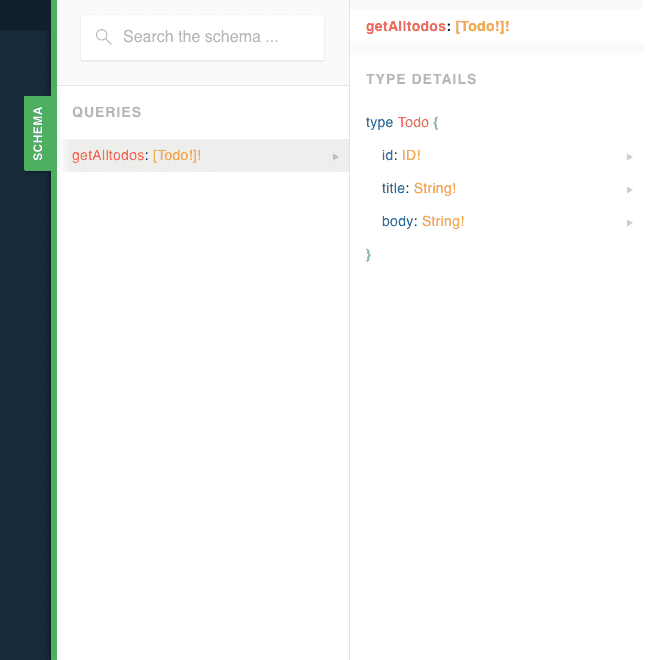
If you click on the left side Schema button you will see a Query which is the same query we created above in Type defs.
As i said getAlltodos Query help us to get the array of todos let’s test it now by
running a query on the graphql playground.
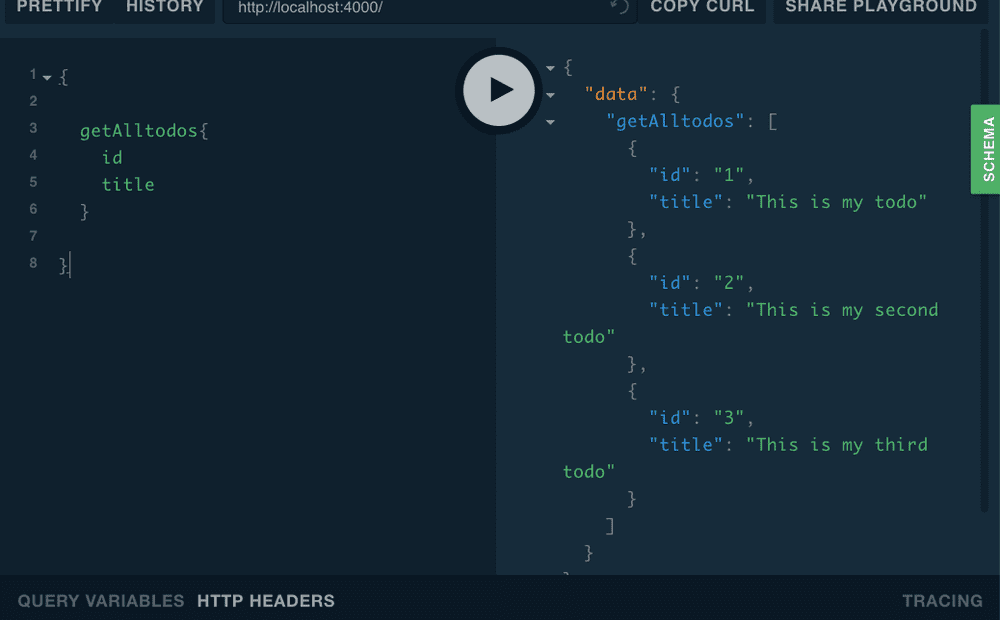
Copy the below query paste on the left side and hit the play button.
{
getAlltodos{
id
title
}
}Response from the graphql server is present on the right-hand side.
Have you seen the flexibility of the graphql we only get the data what we ask not more or not less?
{
getAlltodos{
id
title
body
}
}output
{
"data": {
"getAlltodos": [
{
"id": "1",
"title": "This is my todo",
"body": "sample content in id 1"
},
{
"id": "2",
"title": "This is my second todo",
"body": "sample content in id 2"
},
{
"id": "3",
"title": "This is my third todo",
"body": "sample content in id 3"
}
]
}
}Mutations
Mutations in the graphql allow us to create or update or delete the data.
Let’s add the Mutation types inside the type definitions
const typeDefs = `
type Todo{
id: ID!
title: String!
body: String!
}
type Query{
getAlltodos : [Todo!]!
}
type Mutation{
addTodo(title:String!,body:String!):Todo!,
updateTodo(id:ID!,title:String!,body:String!):Todo!
deleteTodo(id:ID!):Todo!
}
`we have added three Mutation types which are addTodo,updateTodo,deleteTodo
-
addTodoaccepts two arguments which aretitle, bodyand returns back newly created todo. -
updateTodohelps us to update the todo and returns back updated todo. -
deleteTodoonly accept a single argument and returns back deleted todo.
Now, we need to add resolvers to resolve the above mutation types.
const resolvers = {
Query: {
getAlltodos() {
return todos
}
},
Mutation: {
addTodo(parent, args, ctx, info) {
if (args) {
todos.push({
id: Math.random(),
title: args.title,
body: args.body
})
} else {
throw new Error('not args found')
}
return todos[todos.length - 1];
},
updateTodo(parent, args, ctx, info) {
const index = todos.findIndex(e => e.id === +args.id)
let todo = todos[index];
todo.title = args.title
todo.body = args.body
return todos[index]
},
deleteTodo(parent, args, ctx, info) {
const index = todos.findIndex(e => e.id === +args.id)
let todo = todos[index];
const filter = todos.filter(e => e.id !== +args.id)
todos = filter
return todo
}
}
}Every resolver method can have four arguments which are parent, args, context, info
parent: Which helps us to the get parent data if we use Nested queries.
args: Arguments are the objects passed at the time of running the query.
context: This is an object shared by all resolvers Like authentication or change theme
info: It contains the information about the query.
Let’s test our mutations using GraphQL Playground
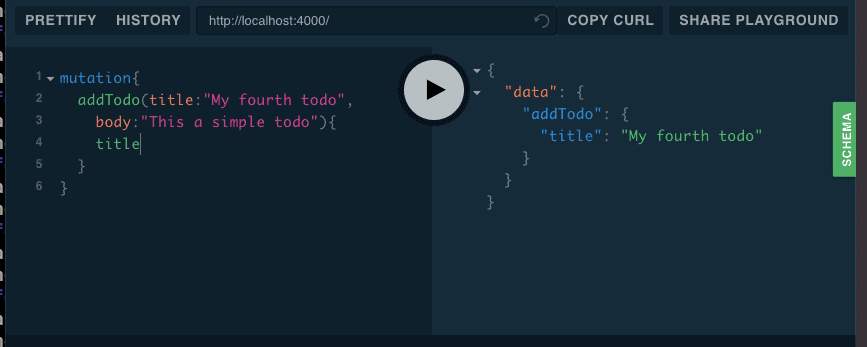
addTodo
mutation{
addTodo(title:"My fourth todo",body:"This a simple todo"){
title
}
}
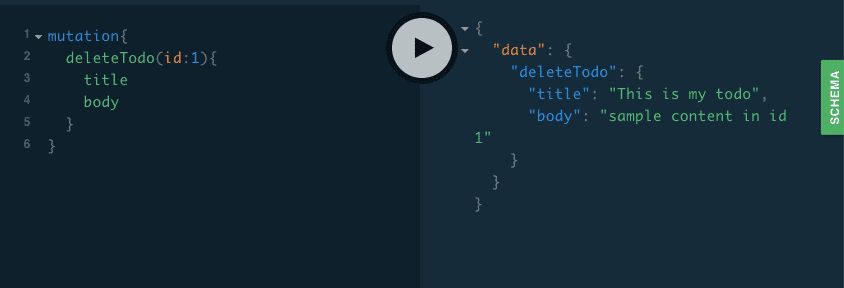
deleteTodo
mutation{
deleteTodo(id:1){
title
body
}
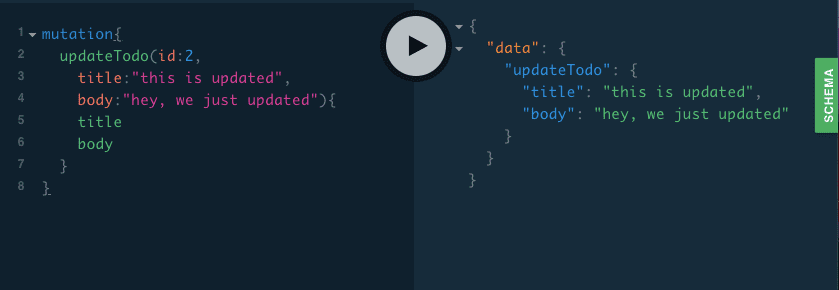
}updateTodo
mutation{
updateTodo(id:2,title:"this is updated",body:"hey, we just updated"){
title
body
}
}Happy coding…