Vue.js Directives List Tutorial with examples
In this tutorial, we are going to learn about different types of VueJS directives with the help of examples.
Contents
What is a Directive ?
A Directive is a special HTML attribute which starts with v-, where it helps to bind javascript expressions.
v-html
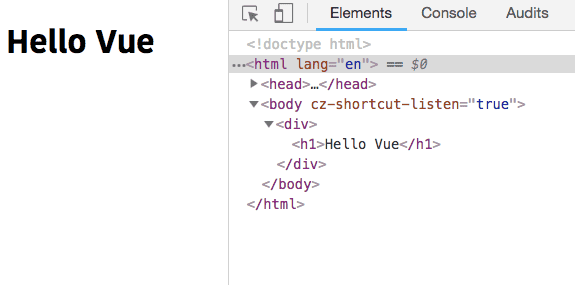
The v-html attribute helps us to interpolate the real html instead of plain text.
example:
<template>
<div v-html="myHTML"></div></template>
<script>
export default{
data:function(){
return{
myHTML: "<h1>Hello Vue</h1>" }
}
}
</script>v-text
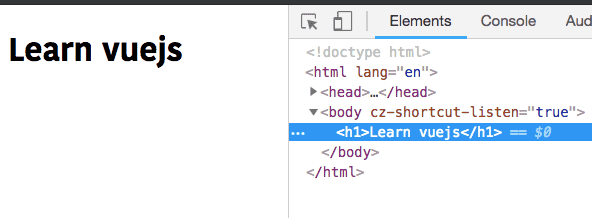
The v-text attribute is used to add the text to an html element.
example:
<template>
<h1 v-text="title"></h1></template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {
title:"Learn vuejs" };
}
};
</script>v-bind
The v-bind directive dynamically binds attribute to a javascript expression.
Binding means substitution of a real value after it has been compiled.
example:
<template>
<div>
<!-- binds src attribute to an expression -->
<img v-bind:src="dogImage" />
<!-- v-bind shorthand syntax -->
<img :src="dogImage" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {
dogImage: "https://i.imgur.com/A8eQsll.jpg" };
}
};
</script>You can also bind other html attributes using v-bind directive.
<a :href="homeUrl">Home</a>
<button :disabled="isActive">Click</button>
<!-- class Binding -->
<div :class="{ red: isRed }"></div>v-on
The v-on directive is used to attach an event listener to an html element.
example:
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{ title }}</h1>
<!-- <button v-on:eventname="eventhandlerName">title</button> -->
<button v-on:click="handleClick">Change title</button> </div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {
title: "Hello"
};
},
methods: {
handleClick: function() {
this.title = "Hello Vue";
}
}
};
</script>We can also pass inline expressions to v-on directive instead of a method.
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{ title }}</h1>
<button v-on:click="title='Hello vue'">Change title</button> </div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {
title: "Hello"
};
}
};
</script>v-model
The v-model directive creates two data binding on a form elements.
example:
<template>
<div>
<input v-model="name" placeholder="Name" /> <p>{{ name }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {
name: "King"
};
}
};
</script>select element
<template>
<form>
<select v-model="rating"> <option disabled value="">Choose your Rating</option>
<option>1</option>
<option>2</option>
<option>3</option>
<option>4</option>
<option>5</option>
</select>
<p>You've rated: {{ rating }}</p>
</form>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {
rating: ""
};
}
};
</script>v-if
The v-if directive allows us to render html elements conditionally based on the truthiness of the expression value.
example:
<template>
<div>
<h1 v-if="isActive">Conditional rendering</h1> <button v-on:click="isActive = !isActive;">Show</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {
isActive: false };
}
};
</script>In the above code, we have added v-if="isActive" to h1 element so that h1 element only render into the dom when isActive is true.
v-for
v-for directive is used to loop over the array of elements and render it into the dom.
example:
<template>
<ul>
<!-- list rendering starts -->
<li v-for="user in users">{{user.name}}</li> </ul>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data:function(){
return{
users:[
{id:1,name:"king"},
{id:2,name:"gowtham"},
{id:3,name:"ooops"},
]
}
}
}
</script>In the above code, we are looping through the users array by using v-fordirective, so that on each iteration user variable is pointing to the different object present inside the array.