How to implement Doubly Linked list Data Structure in JavaScript
In this tutorial, we are going to learn about implementation of doubly linked list in JavaScript
What is Doubly Linked List?
In doubly linked list, each node has a reference to the previous node and the next node. The beginning and ending nodes of the previous and next should point to the null.
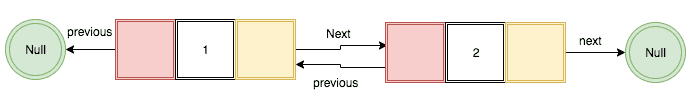
Note: If you don’t know about linked list then please refer to my previous tutorial What is Linked List.
Doubly Linked List Implementation
Let’s implement a doubly linked list.
We are using es6 classes if you don’t about classes then please check out How classes work in javascript
In below code, we created a helper class Node with three properties data, prev, next.
class Node {
constructor(data){
this.data = data; // data
this.prev = null; // reference to the prev node
this.next = null; // . reference to next node
}
}data: The data we need to add in the node.
prev: reference to the previous node.
next: reference to the next node.
The main algorithm starts
class DoublyLinkedList{
constructor(){
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = null;
}
}In the above code, we created a DoublyLinkedList class with three properties
head,tail,length.
head: It is the first node in the List.
tail: Last node in the list.
length: How many nodes present in the list?
Let’s add the functionalities to our DoublyLinked List
Push Method
- Push method helps us to add the new node at the end of the Linked list.
push(data){
const node = new Node(data);
if(!this.head){
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
}else{
node.prev = this.tail;
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node;
}
this.length++;
}- In above code first, we declared a new variable and invoke the Node constructor.
- if there is no this.head then this.head and this.tail to be a new node that we created in step 1.
- If there is already a node
- new node.prev property should be the this.tail
- this.tail.next should be a new node
- updating the tail.
- Increment the length by 1.
Pop method
- It helps us to remove the last node from the list.
In the doubly linked list, it is easy to remove the last node from the list because in the tail property we have the reference to the previous node.
pop(){
if(!this.head) return null
// tail is the last node so that we take the
// prev property from the tail
const prevNode = this.tail.prev
if(prevNode){
prevNode.next = null;
this.tail = prevNode; // updating the tail
}else{
// if prev property is null
// it means there is only single node
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
this.length--; //decrement the length
}-
In above code first, we declared a new variable and store the previous property of the tail.
-
if the previous Node found.
- remove the last node
- updating the tail.
-
if the previous node is null it means we have the only single node
- this.head and this.tail should be null.
-
decrement the length by 1.
insertBeginning.
- insertBeginning method helps us to insert the new node at the beginning of the list.
insertBeginning(data){
// new node is created
const node = new Node(data);
// if there is no nodes
if(!this.head) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
}else{
// update the head.prev to the new node
// take the new node.next property and link it to the
// head property
this.head.prev = node
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
// increment the length
this.length++;
}Remove First method
- The removeFirst method helps us to remove the first node from the linked list.
removeFirst(){
if(!this.head) return null
// storing the second node
const node = this.head.next;
if(node){
// removing the previous node
node.prev = null
// updating the head
this.head = node
}else{
// only single node so we update head and tail to null
this.head = null
this.tail = null
}
//decrement the length
this.length--;
}

