How to create resolvers and query fields in GraphQL (Basics)
In this tutorial, we are going to learn about resolver functions and query fields in GraphQL.
First, let’s design a GraphQL Schema.
type User{
id: ID!
name: String!
}
type Query{
user(id:ID!):User
}Our GraphQL schema has User type with two fields id, name and Query type with one field user but so far graphql didn’t know how to respond to those queries.
Resolvers
-
Resolvers help us to tell the GraphQL, how to respond to the query fields by using a resolver function.
-
In graphql, every query field should be backed by there own resolver function.
This is a resolver function for the user query field in schema.
const resolvers ={
Query:{
user(parent,args,ctx,info){ console.log('hello') return Users.find((user)=> user.id === args.id) } }
}
Note: Resolver function names should be match with the Query field names in the schema.
Every resolver function in GraphQL has four arguments.
parent or root: This helps us to get the parent data if we use nested queries in graphql.
args: Arguments are the objects passed at the time of running the query.
context: The context data is passed to every resolver function, like authentication or change theme.
info: It contains more depth information about the current query. (like Ast’s mostly used in advanced use cases.)
What happens when we run a query?
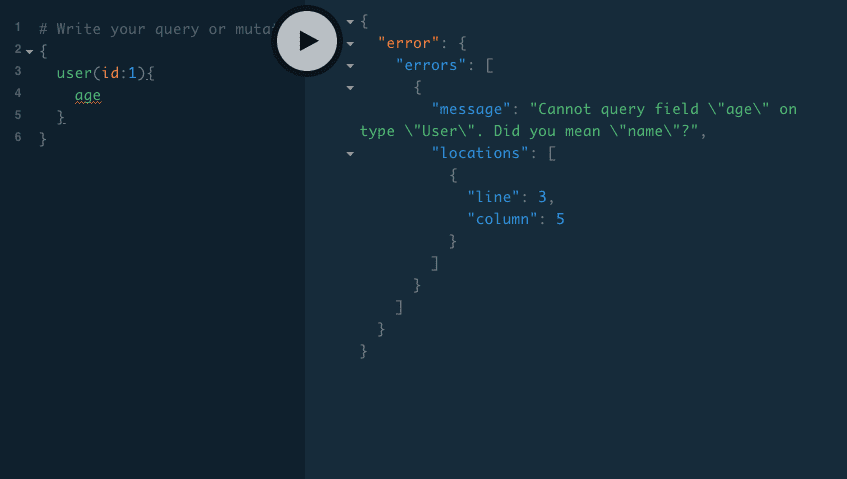
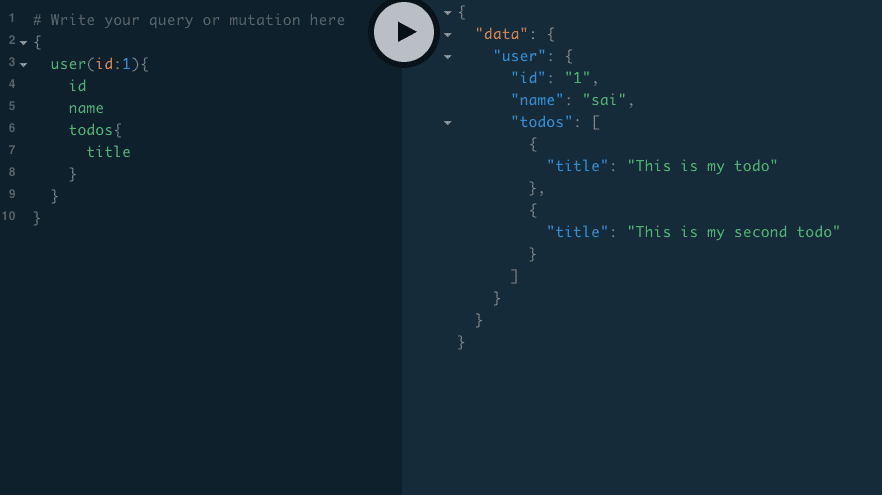
GraphQL first matches the query with the type system if this query is valid then only GraphQL invokes the resolver functions otherwise GraphQL returns the error without invoking a resolver function.
Invalid query
valid query