How to implement Binary search tree Data structure in JavaScript
In this tutorial, we are going to learn about Binary search trees and its implementation in javascript.
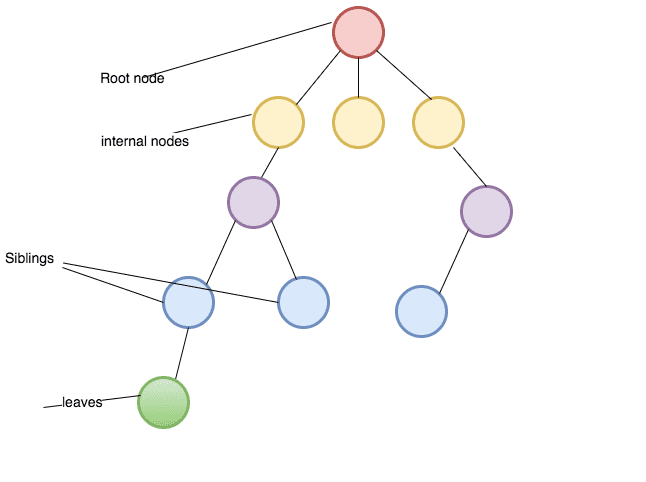
What is a tree?
- A tree is nonlinear data structure compared to stacks and queues, linked lists and arrays which are the linear data structure.
Terminologies used in trees
Root: The top node in a tree.
Child: A node directly connected to another node when moving away from the root.
Parent: The converse notion of a child.
Siblings: A group of nodes with the same parent.
Descendant: A node reachable by repeated proceeding from parent to child. Also known as subchild.
Ancestor: A node reachable by repeated proceeding from child to parent.
Internal nodes: nodes that have children.
External nodes or leaves: nodes that don’t have children.
Types of trees
Binary tree: Every node has at most two children where each node is labeled as being either a left child or a right child
Binary search tree: Every node has at most two children but there is a condition which states that the key in each node must be greater than or equal to any key stored in the left sub-tree, and less than or equal to any key stored in the right sub-tree.
Binary search tree Implementation in Javascript.
class Node{
constructor(data){
this.right = null;
this.left = null;
this.data = data
}
}In the above code we declared a class Node with three properties right, left and data.
Insert method
- It helps us to insert the new node in the correct place.
Pseudocode
- create a new method called insert which accepts the data as its first argument.
- declare and initialize the new variable with that data.
- if the root is empty then set root property to a new node and return it.
- Declare a new variable called current and initialize with root property.
- while the current variable is true
- if the data we passed is equal to current.data then return(no duplicates allowed).
- if data is less than current.data and nothing in left it means we need to set current.left to a new node and break the while loop
- if there is left node then update the current variable to current.left.
- if data is greater than current.data and nothing in right it means we need to set current.right to a new node and break the while loop
- if there is right node then update the current variable to current.right.
class Bst {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
insert(data) {
var node = new Node(data);
if (!this.root) {
this.root = node;
return this;
}
let current = this.root;
while (current) {
// duplicates check
if (data === current.data) {
return;
}
// left node insertion
if (data < current.data) {
if (!current.left) {
current.left = node;
break;
}
current = current.left;
}
//right node insertion
if (data > current.data) {
if (!current.right) {
current.right = node;
break;
}
current = current.right;
}
}
}
}
Find method
- It helps us to find the value present in the binary search tree.
Pseudocode
- Declare a new method called
findwhich accepts data as its first argument. - if the root is empty then return null.
- declare a new variable and initialize with
this.rootproperty. - while current property is true.
- if data is equal to the current. data then return that data.
- if there is
current.rightand the data is greater thancurrent.datathen update the current variable withcurrent.right.
- if there is
current.leftand the data is less thancurrent.datathen update the current variable withcurrent.left.
- return false ( not found anywhere)
find(data){
if(!this.root) return null
let current = this.root;
while(current){
if(data == current.data) return current.data;
if(current.right && data > current.data){
current = current.right
}else{
current = current.left
}
}
return false
}Contains method
The Contains method helps us to check whether the data is present inside the binary search tree or not.
contains(data){
const found = this.find(data)
if(found){
return true
}
return false
}Tree traversal algorithms
Breadth-First Search(Bfs)
Bfs is an algorithm used for traversing in trees or graphs. It starts with a root node of the tree and moves to next level depth.
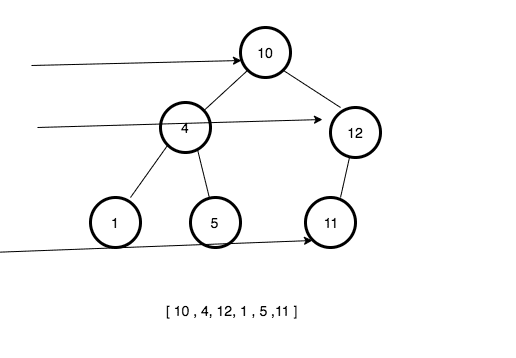
Let’s implement the breadth-first search algorithm in JavaScript.
Pseudocode
- Create a new method called bfs.
- Declare three variables and initialize with a root node, an array with the node, empty array.
- While the queue is not empty.
- update the
nodevariable with the node from the queue. - if
node.leftproperty is true then push node.left to the queue. - if
node.rightproperty is true then push node.right to the queue. - push the data to the finalData array.
- return finalData
bfs(){
let node = this.root;
const queue = [node];
const finalData = [ ]
while(queue.length){
node= queue.shift()
if(node.left) queue.push(node.left)
if(node.right) queue.push(node.right)
finalData.push(node.data)
}
return finalData
}Depth-first search(Dfs)
Preorder traversal
it starts from a root node and moves all the way down to the left before backtracking then all the way right.
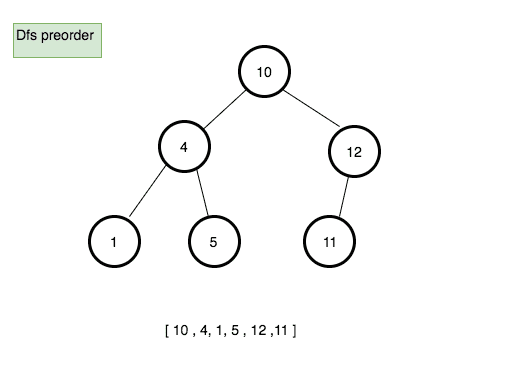
Pseudocode
- Create a new method called preOrder.
- Declare a new variable called finalData and initialize with the empty array.
- create a new function called traverse which accepts node as its first argument.
- push the data present in the node to the finalData array.
- if node.left is true then invoke traverse function with node.left
- if node.right is true then invoke traverse function with node.right
- invoke traverse function with the root node.
- return finalData.
preOrder(){
// final preorder list
const finalData = [];
function traverse(node){
// push the data
finalData.push(node.data)
if(node.left) traverse(node.left)
if(node.right) traverse(node.right)
}
traverse(this.root);
return finalData;
}we are using recursion in the above code.
Postorder traversal
Process all nodes of a tree by recursively processing all subtrees, then finally processing the root.
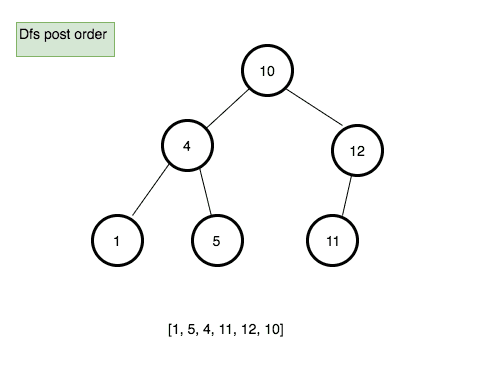
Pseudocode
- Create a new method called postOrder.
- Declare a new variable called finalData and initialize with the empty array.
- create a new function called traverse which accepts node as its first argument.
- if node.left is true then invoke traverse function with node.left.
- if node.right is true then invoke traverse function with node.right.
- push the data present in the node to the finalData array.
- invoke traverse function with the root node.
- return finalData.
postOrder(){
const finalData = [];
function traverse(node){
if(node.left) traverse(node.left)
if(node.right) traverse(node.right)
// push the data
finalData.push(node.data)
}
traverse(this.root)
return finalData
}In-order traversal
Process all nodes of a tree by recursively processing the left subtree, then processing the root, and finally the right subtree.
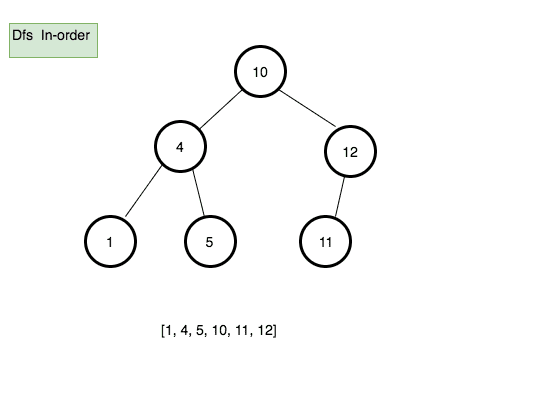
Pseudocode
-
Create a new method called inOrder.
-
Declare a new variable called finalData and initialize with the empty array.
-
create a new function called traverse which accepts node as its first argument.
- if node.left is true then invoke traverse function with node.left.
- push the data present in the node to the finalData array.
- if node.right is true then invoke traverse function with node.right.
-
invoke traverse function with the root node.
-
return finalData.
inOrder(){
const finalData = [];
function traverse(node){
if(node.left) traverse(node.left)
finalData.push(node.data)
if(node.right) traverse(node.right)
}
traverse(this.root)
return finalData
}Max node method
It helps us to find the maximum node in the tree.
Pseudocode
- create a new method called maxNode.
- if root property is empty then return null.
- declare a new variable called current and initialize with this.root.
- while current.right is true.
- update the current to current.right
- return current.data
maxNode(){
if(!this.root) return null;
let current = this.root;
while(current.right){
current = current.right
}
return current.data
}Min node method
It helps us to find the minimum node in the tree.
Pseudocode
- create a new method called maxNode.
- if root property is empty then return null.
- declare a new variable called current and initialize with this.root.
- while current.left is true.
- update the current to current.left.
- return current.data
minNode(){
if(!this.root) return null;
let current = this.root;
while(current.left){
current = current.left
}
return current.data
}



