What is JSX in react detailed
Beginners to the react probably get confused about why we write HTML inside the JavaScript.At the end of this tutorial, you will get a better understanding of jsx.
React without JSX
Let’s write some react code without using jsx so that we can know better , why we use jsx in react.
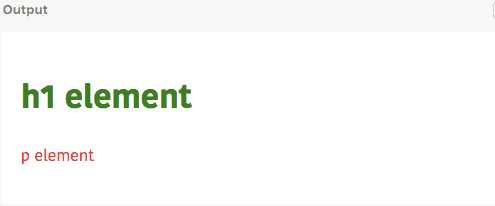
let h1 = React.createElement('h1',{style:{color:"green"}}," h1 element");
let p = React.createElement('p',{style:{color:"red"}},"p element");
let div = React.createElement('div',{className:"container"},h1,p)
ReactDOM.render(div,document.querySelector('#app'))
React.createElement(type,props,children) method takes the three arguments.
type: It means the type of HTML element we need. (example: h1,h2,p,div..etc.)
props: Any properties required for this element/not.
children: The data we need to add inside the html element.(example: plain text or child elements)
React with JSX
Now we are replacing the above code by using jsx.
let green = {color:"green"},
red = {color:"red"}
let h1 = <h1 style ={green}>h1 element</h1>;
let p = <p style={red}>p element</p>;
let div = <div className="container">{h1}{p}</div>
ReactDOM.render(div,document.querySelector('#app'))
The jsx we write inside the react is often converted into JavaScript by using the babel transpiler.
What is JSX?
Jsx allows us to write HTML like syntax inside the JavaScript these is not a react specific thing. By using jsx we can make our code more readable so that react team recommends us to use jsx.
Jsx is not only used in react there are also some other frameworks like preactjs, Infernojs uses jsx.
Expressions in jsx
In jsx, we can embed JavaScript expressions by wrapping with the curly braces {}.
let h1 = <h1> Odd number {2+3}</h1>
let users = ['user1','user2','user3']
let ul = <ul>
{users.map((user,i)=>(
<li>{user}</li>
))}
</ul>
In the above code, we used map method to iterate over the user’s array and created three li elements.
Attributes in jsx
Inline styles
//object
let greenColor = {color:"green"}
let h1 = <h1 style={greenColor}>This is heading</h1>
For inline styling we need to pass style properties as an object inside the curly braces because object is a JavaScript expression.
We can also pass style object directly inside the curly braces instead of using extra variable.
let h1 = <h1 style={{color:"green"}}>This is heading</h1>
External styles using classNames
We need to use className instead of the normal class attribute we use in HTML because there is already a class keyword present inside the JavaScript.
let h1 = <h1 className="header-h1">This is heading</h1>
React Components
The component is a reusable piece of code in react which returns a react element.
function Button(props){
return <button>{props.name}</button>
}
Conditionals in JSX
function ShowHide(props){
if(props.show){
return <button>Show</button>
}else{
return <button>Hide</button>
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<ShowHide show="true" />,document.querySelector('#app'))We can make above component code more simpler by using the ternary operator.
function ShowHide(props){
return <button>{props.show ? "Show": "Hide"}</button>
}Spread operator in jsx
Suppose we need to pass a data to the User component by using props.
function User(props){
return (
<div>
<h1>{props.name}</h1>
<ul>
<li>{props.email}</li>
<li>{props.mobile }</li>
</ul>
</div>
)
}
<User name= "gowtham" email= "user@example.com" mobile= {11233}/>
Let’s pass the same props data by using the spread operator.
let user = {
name:"gowtham",
email:"user@gmail.com",
mobile:2134578
}
<User {...user} />