How to implement hash table in javascript
What is Hashtable?
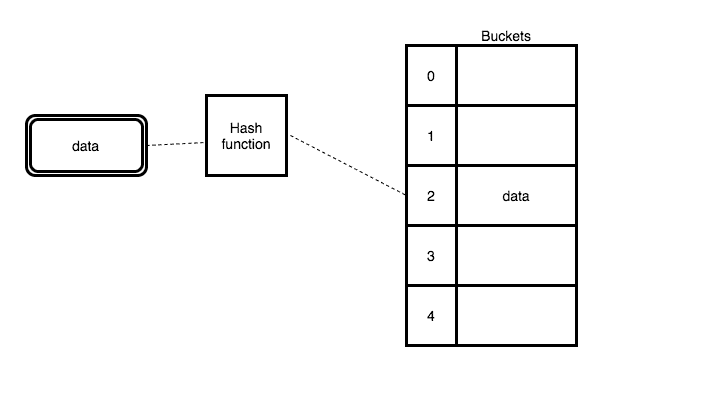
A hash table is a data structure which helps us to quickly find the data by using the keys. Hashtable uses the hash function to generate the indexes sometimes hash function generates the same index for the different data this is called collision.
Definition: A dictionary in which keys are mapped to array positions by hash functions. Having the keys of more than one item map to the same position is called a collision. There are many collision resolution schemes, but they may be divided into open addressing, chaining, and keeping one special overflow area. Perfect hashing avoids collisions but may be time-consuming to create.
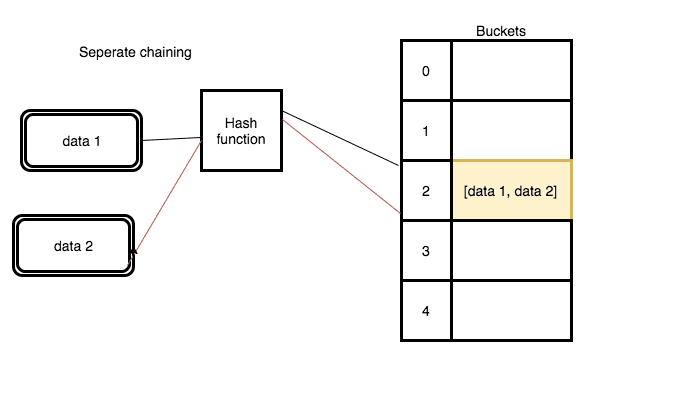
If the collision occurs there are different ways to resolve the collisions.
- Linear Probing
- Separate Chaining
- coalesced chaining
- double hashing
- quadratic probing
In this tutorial, we are using separate chaining to resolve the collisions.
Let’s implement the algorithm
Create a new class called HashTable with two properties buckets and size.
class HashTable{
// default bucket size 42
constructor(size=42){
this.buckets = new Array(size)
this.size = size
}
}Hash function
hash(key){
return key.toString().length % this.size;
}Set method
- It helps us to add the new data to the Hashtable.
Pseudocode
- Create a new method called set which accepts two arguments
keyandvalue. - Hash the key by using a hash function.
- push the key-value pairs into that bucket
set(key,value){
let index = this.hash(key);
if(!this.buckets[index]){
this.buckets[index] = [ ];
}
this.buckets[index].push([key,value])
return index
}Get method
- It helps us to get the data by using the key.
- Create a new method called get which accepts one argument
key. - Hash the key and get the index of that bucket.
- if there is no bucket in that index return null
- for of loop and return value
get(key){
// index of the bucket
let index = this.hash(key);
// if there is no bucket
if(!this.buckets[index])return null
for(let bucket of this.buckets[index]){
// if key matches
if(bucket [0] === key){
// value
return bucket [1]
}
}
}Time complexity
- Insertion - O(1)
- Searching - O(1)
- Deletion - O(1)
Code pen demo
Uses
Several dynamic languages, such as Perl, Python, JavaScript, Lua, and Ruby, use hash tables to implement objects.


