A beginners guide to cross origin resource sharing (CORS)
In this tutorial, we are going to learn about what is cross-origin resource sharing(cors) and how to resolve the cors errors.
What is CORS ?
Cross-origin resource sharing is a security mechanism that prevents you accessing website resources from the different domains or subdomains.
For example, If we try to fetch a data from the example.com to example-24.com you will get a cors error because the origin URL is example.com and you are making the http request to example-24.com.
The origin URL example.com !== example-24.com so that the cross-origin resource sharing policy doesn’t allow you to make http requests to that API endpoint.
Let’s learn it by using an real example.
We are creating a sample server using node and express.
const express = require('express')
const app = express();
app.get('/hello', (req, res) => {
res.json({ name: "reactgo", up: true })
})
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('server is up')
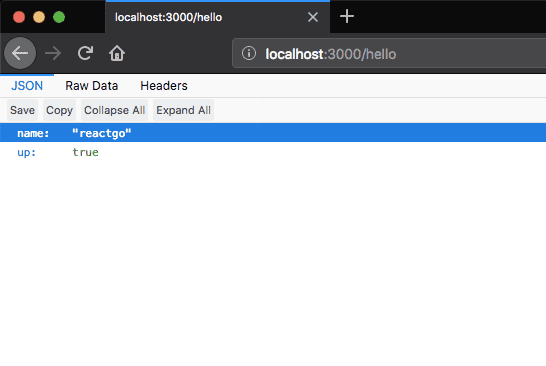
})Now if we open localhost:3000/hello in our browser it will respond with the json object.
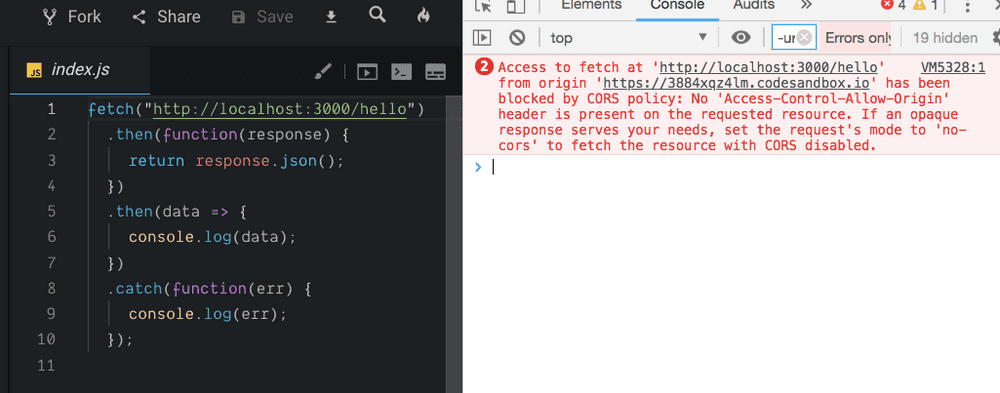
Cors error
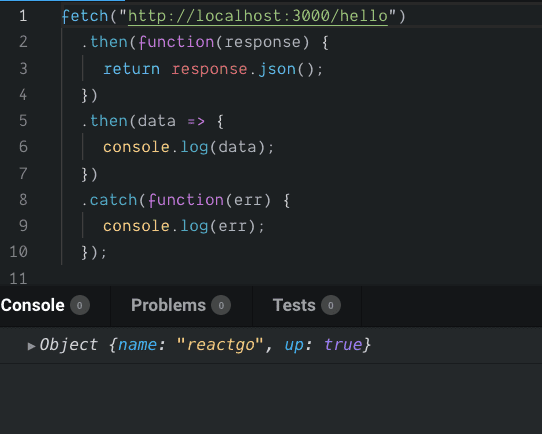
Now, we are fetching the data from the different origin in our frontend app by making an http request to our endpoint localhost:3000/hello.
fetch("http://localhost:3000/hello")
.then(function(response) {
return response.json()
}).then(data=>{
console.log(data)
})
.catch(function(err) {
console.log(err);
});Output
The error is clearly mentioning you are making an http request from the different origin
In the above code, the error has occurred because the user agent made an http request from https://codesandbox.io/s/3884xqz4lm origin to http://localhost:3000/hello so that the response comes the localhost:3000/hello doesn’t contain ‘Access-control-allow-origin’ header.
If the response doesn’t contain ‘Access-control-allow-origin’ header then our user-agent invoke the err callback function.
If the response contains ‘Access-control-allow-origin’ header then our user-agent invoke the response callback function.
How to resolve the cors error?
To resolve the cors error we need to add the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header to our response.
Let’s add the Acess-control-Allow-Origin header to our server.
const express = require('express')
const app = express();
app.use(function (req, res, next) {
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
next();
});
app.get('/hello', (req, res) => {
res.json({ name: "reactgo", up: true })
})
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('server is up')
})We added a middleware to our express server, so that for every response we are sending an Access-Control-Allow-Origin header to the client.
"Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*"* is a wildcard character it means we can fetch the data from the any origin.
Let’s test our API endpoint.
If you open your network tab in chrome dev tools you will see a Request headers and Response headers.
Response headers
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
Connection: keep-alive
Date: Sat, 05 Jan 2019 01:14:49 GMT
ETag: W/"1c-tkTgCcXUYKqMoGefdC0jm6oVXk8"
X-Powered-By: Express
Request headers
Accept: */*
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Accept-Language: en-GB,en-US;q=0.9,en;q=0.8
Connection: keep-alive
Host: localhost:3000
If-None-Match: W/"1c-tkTgCcXUYKqMoGefdC0jm6oVXk8"
Origin: https://3884xqz4lm.codesandbox.ioHow to allow requests only from particular origins?
Sometimes we need to allow requests only from particular origins in that cases we need to specify the origins instead of adding wild * card character.
The express framework provides us a cors middleware which helps us to easily enable the cors.
const express = require('express')
const cors = require('cors')
const app = express();
var corsOptions = {
origin: 'https://3884xqz4lm.codesandbox.io',
optionsSuccessStatus: 200 // some legacy browsers (IE11, various SmartTVs) choke on 204
}
app.use(cors(corsOptions))
app.get('/hello', (req, res) => {
res.json({ name: "reactgo", up: true })
})
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('server is up')
})if we want to allow more than one origin we can do that by passing our origins in an array.
const express = require('express')
const cors = require('cors')
const app = express();
const whitelist = ['https://3884xqz4lm.codesandbox.io',
'http://example2.com']
const corsOptions = {
origin: function (origin, callback) {
if (whitelist.indexOf(origin) !== -1) {
callback(null, true)
} else {
callback(new Error('Not allowed by CORS'))
}
}
}
app.use(cors(corsOptions));
app.get('/hello', (req, res) => {
res.json({ name: "reactgo", up: true })
})
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('server is up')
})What is a preflight request?
Preflight request is an http request issued by the browsers automatically to check whether the requested API endpoint is participating in the cors protocol by including an origin header.
A CORS-preflight request is a CORS request that checks to see if the CORS protocol is understood. It uses
OPTIONSas the method and includes these headers:
The options method contain
Access-Control-Request-Method Indicates that which http method might use when a actual request is made.
Access-Control-Request-Headers Indicates that which http headers the client might send to the server when a actual request is made.
For example, a client is asking a server if POST request is allowed before sending a actual POST request, by using a preflight request.
OPTIONS /user/123
Access-Control-Request-Method: POST
Access-Control-Request-Headers: origin, x-requested-with
Origin: https://example.org
Response from the server
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Connection: keep-alive
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://example.org
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, GET, OPTIONS, DELETE
Access-Control-Max-Age: 63400The Acess-control-Allow-origin-Methods tell us we can also make GET and DELETE requests.
Access-Control-Max-Age: It tells us how long the information provided by the Access-Control-Allow-Methods and Access-Control-Allow-Headers headers can be cached.